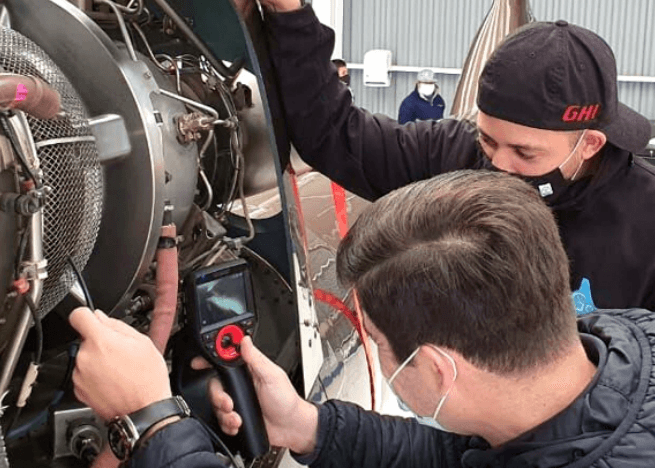
Technology has transformed the way we perform inspections. One of the most essential tools in this category is the inspection camera.
Whether you are a plumber checking pipes, an auto mechanic looking inside engines, or a DIY enthusiast exploring hidden corners of your home, an inspection camera provides real-time visibility where traditional tools fail.
In this article, we’ll break down what an inspection camera is, its varieties, applications, features, benefits, and how to choose the right one for your needs.
What is an Inspection Camera?
An inspection camera (also called a borescope or endoscope) is a device designed to look into spaces that are otherwise inaccessible. It typically consists of:
A flexible or rigid cable
A tiny camera lens at the end
LED lights for illumination
A screen or smartphone connection for real-time viewing
These cameras are designed for professionals and hobbyists alike.
Types of Inspection Cameras
1. Rigid Inspection Cameras
Best for straight-line inspections but limited in flexibility.
2. Flexible Inspection Cameras
Equipped with a bendable cable, ideal for pipes, ducts, and curved passages.
3. Wireless / Wi-Fi Inspection Cameras
These cameras eliminate the need for bulky screens.
4. USB Inspection Cameras
Plug directly into a desktop or mobile device for live feed inspections.
5. Dual-Lens Inspection Cameras
Feature switchable front and Inspection camera side views.
Key Features to Look For
When buying an inspection camera, consider:
Resolution: HD clarity.
Cable Length: From compact models to extended professional tools.
Lighting: Adjustable LED lights for low-light inspections.
Waterproof Rating: IP67+ for plumbing.
Compatibility: Works with dedicated monitors.
Recording Options: Photo and video capture.
Applications of Inspection Cameras
1. Plumbing
Inspection cameras save time on drain inspections.
2. Automotive
Mechanics use them to inspect exhaust systems.
3. Home Maintenance
DIY users can look behind walls.
4. Industrial Maintenance
Factories use inspection cameras for preventive maintenance.
5. Aerospace and Defense
Used to inspect aircraft engines.
6. Medical Field (Specialized Endoscopes)
While not the same as household tools, similar technology is used in endoscopy.
Benefits of Using an Inspection Camera
Accessibility: Reaches confined spaces.
Time-Saving: Faster diagnostics.
Cost-Efficiency: Extends equipment life.
Accuracy: Provides detailed image recording.
Versatility: Adaptable to different needs.
How to Choose the Best Inspection Camera
Define Your Use Case – Plumbing vs automotive vs industrial.
Check Cable Length & Flexibility – Flexible for curves.
Consider Image Quality – HD 1080p cameras recommended.
Select Waterproof & Durable Models – Shockproof casing.
Evaluate Budget & Brand – Check reviews and reliability.
Future Trends in Inspection Cameras
AI-powered Image Analysis for automatic defect detection.
Augmented Reality (AR) Integration for improved visualization.
Ultra-thin & Nano Cameras for medical and microelectronics.
5G & Cloud Connectivity for remote inspection in real-time.
Conclusion
The inspection camera is no longer just a tool—it is a game-changer for professionals and DIY enthusiasts alike. From plumbing and automotive repair to industrial maintenance and aerospace safety, these devices offer a simple yet powerful way to inspect hidden areas.
If you are looking for a way to simplify complex inspections, investing in a high-quality inspection camera is a smart move.